GreenSmart Solutions Pvt Ltd
GreenSmart Solutions (Pvt) Ltd is a leading solar energy solutions provider in Sri Lanka with over 10 years of industry experience. Based in Gampaha, the company specializes in the...
More Details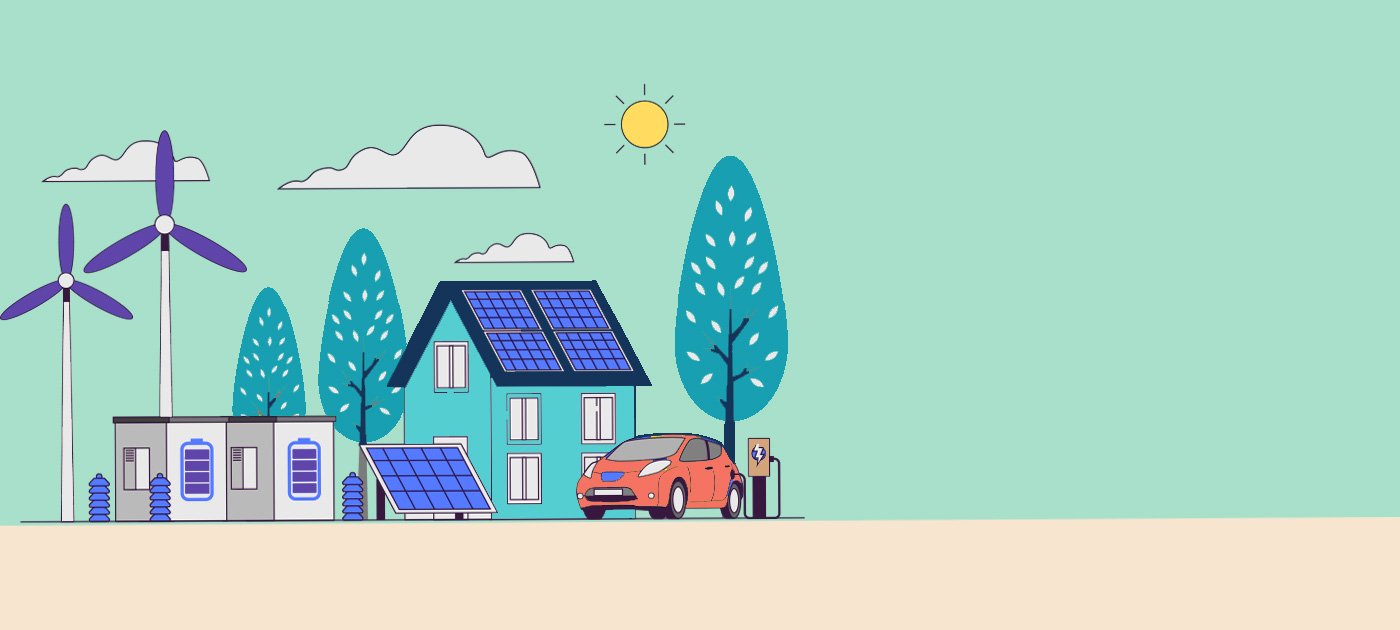

Switching to solar power can be a smart investment for homeowners, but finding the right solar service provider can be a daunting task. By using our website's service, you can easily find and compare local companies to make an informed decision. Take advantage of this helpful resource to find the best solar service provider for your home!

Submit your details


Our team will get in touch with you to gather further information


Your details will be provided to selected solar providers



Each company will evaluate your requirements and contact you separately



Schedule a site survey with our selected provider(s)



Receive your proposal


 1.png)
Get Solar rooftop installed

As energy costs continue to rise and concerns about environmental sustainability grow, many homeowners in Sri Lanka consider residential solar systems as a viable solution. A well-designed solar power system can significantly reduce electricity bills, contribute to environmental sustainability, and even provide a backup power source during outages. This article explores how residential solar systems work, the requirements for setting them up, and the differences between on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid systems, focusing specifically on the Sri Lankan context.

To set up a residential solar system in Sri Lanka, several steps and requirements need to be met:
Description: These systems are connected to the national grid. They supply electricity to the home and feed any excess into the grid.
Pros:
Cons:
Description:These systems are entirely independent of the national grid and rely on batteries to store energy.
Pros:
Cons:
Description:These systems combine features of both on-grid and off-grid systems. They are connected to the grid but also have battery storage.
Pros:
Cons:
Adopting a residential solar system in Sri Lanka can lead to substantial savings on electricity bills, enhance energy security, and contribute to environmental sustainability. Whether opting for an on-grid, off-grid, or hybrid system, working with certified professionals is crucial to ensure a properly designed and installed system. With the proper setup, homeowners can harness the abundant solar energy available in Sri Lanka, positively impacting their finances and the environment.

How Industries can save up to 50% on their energy bills by moving to Solar
Industrial solar solutions differ significantly from their residential counterparts, primarily due to scale and specific energy needs. Here are the main types of solar installations suitable for industrial applications:
While the basic principle remains the same, industrial solar installations differ from residential ones in several key aspects:
While solar power can benefit almost any industry, some sectors stand to gain more:
The potential for cost savings through industrial solar power is substantial. While initial installation costs can be high, industries can save up to 50% on their electricity bills post-installation. For example, a 2 MW solar system factory could reduce monthly electricity expenses from 20 million LKR to about 10 million LKR.
The payback period for industrial solar installations in Sri Lanka typically ranges from 3 to 4 years. Efficient project designs and use of high-quality components contribute to favorable ROI.
The upfront costs for a factory-sized solar installation can be significant. Still, financing options from local banks, such as Commercial Bank, HNB, and Bank of Ceylon, help mitigate these costs. Interest rates vary based on the client's creditworthiness, ranging from single digits to around 12-13%.
Billing Solutions
For factories with high energy consumption, Net Metering is typically the best option as it allows for offsetting energy usage with the electricity generated by their solar panels. Net Accounting might benefit warehouses with lower energy consumption since excess energy is sold back to the grid.
Revenue Generation
Net Accounting and Net Plus models allow factories to generate revenue by returning excess energy to the grid. This is particularly advantageous for industries with large roof spaces capable of hosting extensive solar arrays.
Industries can significantly reduce their carbon footprint by utilizing solar energy. By installing solar panels, companies can switch to a clean, renewable energy source, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels. Adopting solar energy helps industries meet their corporate social responsibility (CSR) and sustainability goals. This not only helps in lowering electricity bills but also in building an environmentally friendly image.
Solar energy enhances energy security and independence for factories. Hybrid systems with battery storage are particularly beneficial during power cuts or rainy days, providing a reliable power supply and reducing dependence on the national grid.
While the benefits are clear, industries must also consider challenges:
Efficient project designs and planning, coupled with the use of high-quality equipment, can yield a substantial ROI for industries, according to Chamil Silva, Co-Founder and Managing Director of Solar Ray Energy. In a groundbreaking achievement, Solar Ray recently completed a 2.2 MW rooftop solar project that not only promises to save the client 30-40 million rupees in the long term but also accomplished the unprecedented feat of eliminating the need for an additional transformer. This innovative approach sets a new standard in the industry for cost-effective and efficient solar installations.
The project leveraged high-efficiency 665-watt panels to maximize energy generation in space-constrained environments, demonstrating Solar Ray's commitment to cutting-edge solutions.
Silva notes that a typical solar installation project on an industrial site can take about 3 to 4 months from initiation to completion, encompassing site assessment, design, obtaining necessary approvals, installation, and commissioning. This timeline, combined with the long-term savings and innovative design, showcases the practicality and efficiency of Solar Ray's approach to industrial solar solutions.
Post-installation support and maintenance play a crucial role in maximizing the efficiency of solar installations. When high-quality products are used, the need for frequent replacements and maintenance is minimal. However, the implementation of robust monitoring systems, a standard feature in all of Solar Ray's industrial projects, is essential. These systems enable prompt detection and resolution of any issues, while also facilitating performance optimization. This proactive approach ensures that your solar installation consistently operates at peak efficiency, delivering maximum value over its lifetime.
Founded in 2016, Solar Ray Energy specializes in rooftop solar solutions for commercial and residential applications. Mr. Silva, with nearly two decades of experience in renewable energy, has been involved in various leadership roles and advisory capacities across multiple organizations, including the Sustainable Energy Authority and the Ministry of Power and Energy in Sri Lanka.
As energy costs continue to rise and environmental regulations tighten, industrial solar power is becoming less of an option and more of a necessity. By carefully assessing their energy needs, physical infrastructure, and local regulations, industries can leverage solar power to significantly reduce their electricity bills. The initial investment may be substantial, but the long-term savings, coupled with the positive environmental impact, make solar an increasingly attractive option for industries of all sizes. As technology advances and costs continue to fall, we can expect to see solar panels becoming as common on factory roofs as they are on residential homes.
To get proposals and quotations from reputable solar providers for your industrial solar needs, simplay visit the Ideal Home’s Solar page and submit your details.

GreenSmart Solutions (Pvt) Ltd is a leading solar energy solutions provider in Sri Lanka with over 10 years of industry experience. Based in Gampaha, the company specializes in the...
More Details
Wontec Lanka (Pvt) Ltd is a rapidly growing solar energy solutions provider in Sri Lanka, committed to delivering innovative and sustainable power solutions for residential, commercial,...
More Details
Our Vision As a pioneering renewable energy enterprise, our vision is to lead with innovation and offer competitive solutions. We provide comprehensive products and services that match...
More DetailsEvery home is unique and requires specific consideration. Let us help you figure out which type of solar panel will serve your purpose.
This solar system operates on a plant that is linked to a network or framework via a meter system that counts energy consumption and does not have a backup bank.
The only component of this solar system is a battery bank. It is said to be ideal for remote or rural locations.
This sort of solar system generates solar energy while also providing backup power in the event of a power outage.
 Frequently asked questions
Frequently asked questionsFor any assistance or enquiry, please feel free to reach out to us. We’d love to help!